NCERT Solutions Ch-8 Introduction to Trigonometry
Chapter 8 of Class 10 Maths, “Introduction to Trigonometry,” lays the foundation of trigonometry, focusing on the relationships between angles and sides in a right-angled triangle. This chapter introduces students to key trigonometric ratios—sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent—defined using the sides of a right triangle. It also explains how to calculate these ratios for standard angles like 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°, which helps in solving real-world problems in fields such as physics and engineering. Additionally, the chapter explores trigonometric identities, giving students tools for simplifying expressions and solving various mathematical problems. Understanding these concepts is crucial for advanced studies in mathematics and other technical fields.
NCERT Solutions Maths Ch-8 Introduction to Trigonometry Exercise 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 and 8.4
We try to teach you all Questions in easy way. We solve all chapter wise sums of maths textbook. In every chapter include NCERT solutions. For solutions of Exercise 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 and 8.4 click on Tabs :
Question 1.
In ∆ABC right angled at B, AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 cm. Determine:
(i) sin A, cos A
(ii) sin C, cos C
Solution:

Question 2.
In given figure, find tan P – cot R.
Solution:

Question 3.
If sin A =  , calculate cos A and tan A.
, calculate cos A and tan A.

Question 4.
Given 15 cot A = 8, find sin A and sec A.
Solution:

Question 5.
Given sec θ = 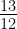 , calculate all other trigonometric ratios.
, calculate all other trigonometric ratios.
Solution:
Let us assume a right angled triangle ABC, right angled at B
sec θ =13/12 = Hypotenuse/Adjacent side = AC/AB
According to the Pythagoras theorem,
AC2=AB2 + BC2
Substitute the value of AB and AC
(13k)2= (12k)2 + BC2
169k2= 144k2 + BC2
169k2= 144k2 + BC2
BC2 = 169k2 – 144k2
BC2= 25k2
Therefore, BC = 5k
Now, substitute the corresponding values in all other trigonometric ratios
So,
Sin θ = Opposite Side/Hypotenuse = BC/AC = 5/13
Cos θ = Adjacent Side/Hypotenuse = AB/AC = 12/13
tan θ = Opposite Side/Adjacent Side = BC/AB = 5/12
Cosec θ = Hypotenuse/Opposite Side = AC/BC = 13/5
cot θ = Adjacent Side/Opposite Side = AB/BC = 12/5
Question 6.
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠A = ∠B.
Solution:

Question 7.
If cot θ = 7/8, evaluate :
(i) (1 + sin θ)(1 – sin θ)/(1+cos θ)(1-cos θ)
(ii) cot2 θ
Solution:
Let us assume a △ABC in which ∠B = 90° and ∠C = θ
Given:
cot θ = BC/AB = 7/8
Let BC = 7k and AB = 8k, where k is a positive real number
According to Pythagoras theorem in △ABC we get.
AC2 = AB2+BC2
AC2 = (8k)2+(7k)2
AC2 = 64k2+49k2
AC2 = 113k2
AC = √113 k
According to the sine and cos function ratios, it is written as
sin θ = AB/AC = Opposite Side/Hypotenuse = 8k/√113 k = 8/√113 and
cos θ = Adjacent Side/Hypotenuse = BC/AC = 7k/√113 k = 7/√113
Now apply the values of sin function and cos function:

Question 8.
If 3 cot A = 4, check whether  = cos² A – sin² A or not.
= cos² A – sin² A or not.
Solution:

Question 9.
In triangle ABC, right-angled at B, if tan A = 1/√3 find the value of:
(i) sin A cos C + cos A sin C
(ii) cos A cos C – sin A sin C
Solution:

Question 10.
In ∆ PQR, right-angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Determine the values of sin P, cos P and tan P
Solution:
In a given triangle PQR, right angled at Q, the following measures are
PQ = 5 cm
PR + QR = 25 cm
Now let us assume, QR = x
PR = 25-QR
PR = 25- x
According to the Pythagorean Theorem,
PR2 = PQ2 + QR2
Substitute the value of PR as x
(25- x) 2 = 52 + x2
252 + x2 – 50x = 25 + x2
625 + x2-50x -25 – x2 = 0
-50x = -600
x= -600/-50
x = 12 = QR
Now, find the value of PR
PR = 25- QR
Substitute the value of QR
PR = 25-12
PR = 13
Now, substitute the value to the given problem
(1) sin p = Opposite Side/Hypotenuse = QR/PR = 12/13
(2) Cos p = Adjacent Side/Hypotenuse = PQ/PR = 5/13
(3) tan p =Opposite Side/Adjacent side = QR/PQ = 12/5
11. State whether the following are true or false. Justify your answer.
(i) The value of tan A is always less than 1.
(ii) sec A = 12/5 for some value of angle A.
(iii)cos A is the abbreviation used for the cosecant of angle A.
(iv) cot A is the product of cot and A.
(v) sin θ = 4/3 for some angle θ.
Solution:
(i) The value of tan A is always less than 1.
Answer: False
Proof: In ΔMNC in which ∠N = 90∘,
MN = 3, NC = 4 and MC = 5
Value of tan M = 4/3 which is greater than.
The triangle can be formed with sides equal to 3, 4 and hypotenuse = 5 as it will follow the Pythagoras theorem.
MC2=MN2+NC2
52=32+42
25=9+16
25 = 25
(ii) sec A = 12/5 for some value of angle A
Answer: True
Justification: Let a ΔMNC in which ∠N = 90º,
MC=12k and MB=5k, where k is a positive real number.
By Pythagoras theorem we get,
MC2=MN2+NC2
(12k)2=(5k)2+NC2
NC2+25k2=144k2
NC2=119k2
Such a triangle is possible as it will follow the Pythagoras theorem.
(iii) cos A is the abbreviation used for the cosecant of angle A.
Answer: False
Justification: Abbreviation used for cosecant of angle M is cosec M. cos M is the abbreviation used for cosine of angle M.
(iv) cot A is the product of cot and A.
Answer: False
Justification: cot M is not the product of cot and M. It is the cotangent of ∠M.
(v) sin θ = 4/3 for some angle θ.
Answer: False
Justification: sin θ = Height/Hypotenuse
We know that in a right angled triangle, Hypotenuse is the longest side.
∴ sin θ will always less than 1 and it can never be 4/3 for any value of θ.
Question 1.
Evaluate the following:


Question 2.
Choose the correct option and justify your choice:


Question 3.
If tan (A + B) = √3 and tan (A – B) = 1/√3 ,0° < A + B ≤ 90°; A > B, find A and B.
Solution:
tan (A + B) = √3
Since √3 = tan 60°
Now substitute the degree value
⇒ tan (A + B) = tan 60°
(A + B) = 60° … (i)
The above equation is assumed as equation (i)
tan (A – B) = 1/√3
Since 1/√3 = tan 30°
Now substitute the degree value
⇒ tan (A – B) = tan 30°
(A – B) = 30° … equation (ii)
Now add the equation (i) and (ii), we get
A + B + A – B = 60° + 30°
Cancel the terms B
2A = 90°
A= 45°
Now, substitute the value of A in equation (i) to find the value of B
45° + B = 60°
B = 60° – 45°
B = 15°
Therefore A = 45° and B = 15°
Question 4.
State whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer.
(i) sin (A + B) = sin A + sin B.
(ii) The value of sin θ increases as θ increases.
(iii) The value of cos θ increases as θ increases.
(iv) sin θ = cos θ for all values of θ.
(v) cot A is not defined for A = 0°.
Solution:

Question 1.
Evaluate:
![]()

Question 2.
Show that:
(i) tan 48° tan 23° tan 42° tan 67° = 1
(ii) cos 38° cos 52° – sin 38° sin 52° = 0
Solution:

Question 3.
If tan 2A = cot (A – 18°), where 2A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
Solution:
tan 2A = cot (A- 18°)
We know that tan 2A = cot (90° – 2A)
Substitute the above equation in the given problem
⇒ cot (90° – 2A) = cot (A -18°)
Now, equate the angles,
⇒ 90° – 2A = A- 18° ⇒ 108° = 3A
A = 108° / 3
Therefore, the value of A = 36°
Question 4.
If tan A = cot B, prove that A + B = 90°.
Solution:
tan A = cot B
We know that cot B = tan (90° – B)
To prove A + B = 90°, substitute the above equation in the given problem
tan A = tan (90° – B)
A = 90° – B
A + B = 90°
Question 5.
If sec 4A = cosec (A – 20°), where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
Solution:
sec 4A = cosec (A – 20°)
We know that sec 4A = cosec (90° – 4A)
To find the value of A, substitute the above equation in the given problem
cosec (90° – 4A) = cosec (A – 20°)
Now, equate the angles
90° – 4A= A- 20°
110° = 5A
A = 110°/ 5 = 22°
Therefore, the value of A = 22°
Question 6.
If A, B and C are interior angles of a triangle ABC, then show that
sin (B+C/2) = cos A/2
Solution:
We know that, for a given triangle, sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is equal to 180°
A + B + C = 180° ….(1)
To find the value of (B+ C)/2, simplify the equation (1)
⇒ B + C = 180° – A
⇒ (B+C)/2 = (180°-A)/2
⇒ (B+C)/2 = (90°-A/2)
Now, multiply both sides by sin functions, we get
⇒ sin (B+C)/2 = sin (90°-A/2)
Since sin (90°-A/2) = = cos A/2, the above equation is equal to
sin (B+C)/2 = cos A/2
Question 7.
Express sin 67° + cos 75° in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles between 0° and 45°.
Solution:
Given:
sin 67° + cos 75°
In term of sin as cos function and cos as sin function, it can be written as follows
sin 67° = sin (90° – 23°)
cos 75° = cos (90° – 15°)
= sin (90° – 23°) + cos (90° – 15°)
Now, simplify the above equation
= cos 23° + sin 15°
Therefore, sin 67° + cos 75° is also expressed as cos 23° + sin 15°
Question 1.
Express the trigonometric ratios sin A, sec A and tan A in terms of cot A.
Solution:

Question 2.
Write all the other trigonometric ratios of ∠A in terms of sec A.
Solution:

Question 3.
Evaluate:


Question 4.
Choose the correct option. Justify your choice.
(i) 9 sec2A – 9 tan2A =
(A) 1 (B) 9 (C) 8 (D) 0
(ii) (1 + tan θ + sec θ) (1 + cot θ – cosec θ)
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) – 1
(iii) (sec A + tan A) (1 – sin A) =
(A) sec A (B) sin A (C) cosec A (D) cos A
(iv) 1+tan2A/1+cot2A =
(A) sec2 A (B) -1 (C) cot2A (D) tan2A
Solution:

Question 5.
Prove the following identities, where the angles involved are acute angles for which the expressions are defined.

Solution:







