In Chapter 1 of the NCERT Science textbook for Class 10, titled “Chemical Reactions and Equations,” students learn about the nature of chemical reactions, the types of chemical changes, and how to represent these reactions through equations. The chapter emphasizes the importance of balancing chemical equations to comply with the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Key concepts include the identification of reactants and products, various types of reactions (like combination, decomposition, displacement, and redox reactions), and practical applications of these reactions in everyday life. The chapter also discusses the significance of coefficients and states of matter in chemical equations, providing students with a foundational understanding of chemical processes that is essential for further studies in chemistry.
NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions And Equations
Page Number: 6
Question 1
Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air ?
Answer:
Magnesium gets covered with a layer of magnesium oxide when kept in air for a long time. This layer hinders the burning of magnesium. Hence, it is to be cleaned before burning.
Question 2
Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
(i) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
(ii) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
(iii) Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Answer:
(i) H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
(ii) 3 BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → BaSO4 + 2 AlCl3
(iii) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2↑
Question 3
Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions :
(i) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
(ii) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Answer:
(i) BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl (aq)
(ii) NaOH (aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Page Number: 10
Question 1
A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for white washing.
(i) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (i) above with water.
Answer:
(i) The substance whose solution in water is used for white washing is calcium oxide (or quick lime). Its formula is CaO.

Question 2
Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in text book Activity 1.7 (i.e., electrolysis of water) double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas. [CBSE 2015 (Delhi)]
Answer:
In Activity 1.7, water is electrolysed to give H2 gas at one electrode and O2 gas at the other electrode.
2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Thus two molecules of water on electrolysis give two molecules of hydrogen gas and one molecule of oxygen gas or in other words the amount of hydrogen gas collected would be double than that of oxygen gas.
Page Number: 13
Question 1
Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it ?
OR
An iron nail is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate for about 30 minutes. State the change in colour observed. Give reason for the change. [CBSE 2015 (Delhi)]
Answer:
When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, the displacement reaction takes place. The colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of light green solution of iron sulphate.
![]()
Question 2
Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10 (NCERT Text Book).
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid react to form sodium chloride and water.
![]()
Question 3
Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances which are reduced in the following reactions.
(i) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
(ii) CuO (s) + H2(g) → Cu (s) + H2O(l)
Answer:
(i) Substances oxidised is Na as it gains oxygen and oxygen is reduced.
(ii) Substances reduced is Cu as hydrogen is oxidised as it gains oxygen.
Textbook Question
Question 1
Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect ?
2 PbO(s) + C(s) → 2Pb (s) + CO2(g)
(a) Lead is getting reduced.
(b) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised.
(c) Carbon is getting oxidised.
(d) Lead oxide is getting reduced.
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c)
(iv) All
Answer:
(i) (a) and (b)
Question 2
Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a
(a) combination reaction
(b) double displacement reaction
(c) decomposition reaction
(d) displacement reaction
Answer:
(d) Displacement reaction.
Question 3
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings ? Tick the correct answer :
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(b) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c) No reaction takes place.
(d) Iron salt and water are produced.
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
Question 4
What is a balanced chemical equation ? Why should chemical equations be balanced ?
Answer:
A balanced chemical equation has an equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products.
The chemical equations should be balanced to satisfy the law of conservation of mass.
Question 5
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Answer:
(a) 3H2 (g) + N2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
(b) H2S (g) + 3O2 (g) → SO2 (g) + 2H2O(l)
(c) 3BaCl2 (aq) + Al2(SO4)3 (aq) → 2AlCl3 (aq) + 3BaSO4 ↓(s)
(d) 2K (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2KOH (aq) + H2 (g)
Question 6
Balance the following chemical equations :
(a) HNO3 + Ca (OH)2 → Ca (NO3)2 + H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
Answer:
(a) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(b) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
Question 7
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions :
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate + Water
(b) Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver
(c) Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper
(d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Answer:
(a) Ca (OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(b) Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2 Ag
(c) 2Al + 3 CuCl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3 Cu
(d) BaCl2 + K2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2KCl
Question 8
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case :
(a) Potassium bromide (aq) + Barium iodide (aq) → Potassium iodide (aq) + Barium
(b) Zinc carbonate(s) → Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide (g) bromide(s)
(c) Hydrogen (g) + Chloride (g) → Hydrogen chloride (g)
(d) Magnesium (s) + Hydrochloric acid (aq) → Magnesium chloride (aq) + Hydrogen (g)
Answer:
(a) 2KBr (aq) + Bal2(aq) → 2Kl(aq) + BaBr2(s)
Type : Double displacement reaction
(b) ZnCO3 (s) → ZnO (s) + CO2 (g)
Type : Decomposition reaction
(c) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g)
Type : Combination reaction
(d) Mg (s) + 2HCl (aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Type : Displacement reaction
Question 9
What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions ? Give examples.
Answer:
Exothermic reactions : Those reactions in which heat is evolved are known as exothermic reactions. An exothermic reaction is indicated by writing “+ Heat”on the products side of an equation.
Example :
(i) C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + Heat
(ii) N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g) + Heat
Endothermic reactions : Those reactions in which heat is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions. An endothermic reaction is usually indicated by writing “Heat” on the product side of a chemical equation.
Examples :
(i) C (s) + 2S (s) → CS2 (l) – Heat
(ii) N2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO(g) – Heat
Question 10
Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction ? Explain.
Answer:
Respiration is an exothermic process because during respiration glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of our body to form carbon dioxide and water along with the production of energy.![]()
Question 11
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
In a decomposition reaction, a single compound breaks down to produce two or more simpler substances.
For example: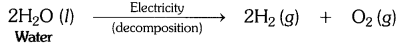
While, in a combination reaction, two or more substances simply combine to form a new substance.
For example:![]()
Question 12
Write one equation each for the decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
OR
Decomposition reactions require energy either in the form of heat or light or electricity for breaking down the reactants. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity. [CBSE 2015 (Delhi)]
Answer: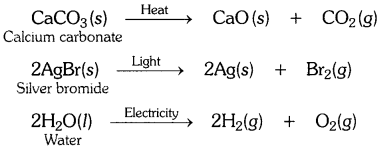
Question 13
What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
In displacement reactions, a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its solution. For example,
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq)
This is a displacement reaction where iron displaces copper from its solution.
In double displacement reactions, two reactants in solution exchange their ions. For example,
AgNO3(aq) + NaCl (aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3 (aq)
This is a double displacement reaction where silver nitrate and sodium chloride exchange Cl– and NO3– ions between them.
Question 14
In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Answer:![]()
Question 15
What do you mean by a precipitation reaction ? Explain by giving examples.
Answer:
A reaction in which an insoluble solid called precipitate is formed that separates from the solution is called a precipitation reaction.
Example : When a solution of iron (III) chloride and ammonium hydroxide are mixed, a brown precipitate of iron (III) hydroxide is formed.![]()
Question 16
Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each:
(a) Oxidation and
(b) Reduction.
Answer:
(a) Oxidation : The addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation.
Example :
(i) S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) (Addition of oxygen to sulphur)
(ii) 2Mg(s) + O2 (g) → 2MgO(s) (Addition of oxygen to magnesium)
(b) Reduction : The removal of oxygen from a substance is called reduction.
Example: (i) CuO + H2 𝐻𝑒𝑎𝑡−→−− Cu + H2O
Here, copper oxide is being reduced to copper because oxygen gets removed from copper oxide.
(ii) ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Here, zinc oxide is being reduced to zinc because oxygen gets removed from zinc oxide.
Question 17
A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Answer:
Element ‘X’ is copper (Cu).
The black coloured compound is copper oxide (CuO). The reaction involved is![]()
Question 18
Why do we apply paint on iron articles ?
Answer:
Paint does not allow iron articles to come in contact with air, water and saves iron articles from damage due to rusting.
Question 19
Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why ?
Answer:
To keep food items fresh and save from getting oxidised, food items are flushed with nitrogen.
Question 20
Explain the following terms with one example each (a) Corrosion, (b) Rancidity.
Answer:
(a) Corrosion : It is the process in which metals are eaten up gradually by the action of air, moisture or a chemical (such as an acid) on their surface.
Example : When iron is exposed to moist air for a long period of time, its surface acquires a coating of a brown, flaky substance called rust. Rust is mainly hydrated iron (III) oxide [Fe2O3.xH20].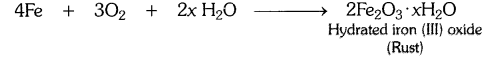
(b) Rancidity : The condition produced by aerial oxidation of fats and oils in foods marked by unpleasant smell and taste is called rancidity.
Rancidity spoils the food materials prepared in fats and oils which have been kept for a considerable time and makes them unfit for eating.
Rancidity can be prevented by adding anti-oxidants to foods containing fats and oils. It can also be prevented by flushing fat and oil containing foods with nitrogen before sealing.
